Blink
This guide will walkthrough the native compilation of a Blink executable for the phyCORE-AM62Ax Development Kit running Linux. This demo will blink an LED connected to WKUP_CLKOUT0 processor pad, which is accessible at pin 9 of the X17 Expansion Connector (with net name X_WKUP_CLKOUT0). In order for this demo to work properly we will also need to dive into configuring processor pins and the best reference for that is the Technical Reference Manual (TRM) and Datasheet for the AM62Ax processor, which can be downloaded from the Texas Instruments AM62Ax product page.
Note
This guide leverages build tools on the target (native compilation). These are not installed by default and must be first added to the target software. Checkout the Hello World guide for steps on adding this support.
Create the Blink Program
Let’s make a project directory to contain the Blink source code:
Target (Linux)
mkdir ~/blink-project
cd ~/blink-project
Create the main Blink application source code file using your favorite text editor:
Target (Linux)
vi blink.c
Note
The vi text editor begins in “Command Mode” and you must first hit the ‘i’ key in order to enter “Insert Mode”. Using the arrow keys to navigate, make the necessary changes and then hit ESC to go back to “Command mode”. Now enter “:wq” to write the file and quit.
Pro Tip: Use the right click on your mouse to paste! This will only work if you are in “Insert Mode” first.
Edit the contents of the file to reflect the following and remember to save your changes when you are done!
blink.c
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
// Setup MCU_GPIO0_23 (NET X_WKUP_CLKOUT0)
#define MCU_GPIO0_ADDR_START 0x0004201000
#define MCU_GPIO0_ADDR_END 0x0004201100
#define MCU_GPIO0_SIZE (MCU_GPIO0_ADDR_END - MCU_GPIO0_ADDR_START)
#define MCU_GPIO0_PORT (1 << 23)
#define GPIO_DATA_OFFSET 0x000000018
#define GPIO_DIR_OFFSET 0x000000010
#define GPIO_CLEAR_OFFSET 0x00000001C
void *gpioAddress;
unsigned int *gpio_setdataout_addr;
unsigned int *gpio_direction_addr;
unsigned int *gpio_cleardata_addr;
void delay(unsigned long ms)
{
clock_t start_ticks = clock();
unsigned long millis_ticks = CLOCKS_PER_SEC / 1000;
while (clock() - start_ticks < ms * millis_ticks){}
}
int main()
{
int fd = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR);
gpioAddress = mmap(0, MCU_GPIO0_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, MCU_GPIO0_ADDR_START);
close(fd);
gpio_setdataout_addr = gpioAddress + GPIO_DATA_OFFSET;
gpio_direction_addr = gpioAddress + GPIO_DIR_OFFSET;
gpio_cleardata_addr = gpioAddress + GPIO_CLEAR_OFFSET;
*gpio_direction_addr &= ~(MCU_GPIO0_PORT);
while (1)
{
*gpio_setdataout_addr |= MCU_GPIO0_PORT;
delay(1000);
*gpio_cleardata_addr |= MCU_GPIO0_PORT;
delay(1000);
}
}
Compile the project using the GCC toolchain, which you had to manually add to the phytec-qt5demo-image. See the Hello World guide for more nformation.
Target (Linux)
gcc -O blink.c -o blink
You should now see an executable of the name “blink” in the current working directory.
Mux the Processor Pin
In order for this blink executable to work as intended, we will also need to multiplex (AKA mux) the processor pad such that the MCU_GPIO0_23 signal is enabled and configured as an output on the WKUP_CLKOUT0 processor pad. We can do this easily using the ‘devmem2’ utility to directly access nd modify the AM62Ax hardware registers.
Warning
Use caution when working with the ‘devmem2’ utility as it gives you direct access to read and write to memory that could render the system unstable if you modify memory that is being actively used. This utility has no error checking and shouldn’t be relied upon in production software. PHYTEC recommends working with ‘devmem2’ only while prototyping and transitioning your pin settings to the linux device tree for production.
First, identify the processor pad that brings out the signal we are targeting. This can be done by following X_WKUP_CLKOUT0 in the carrier board schematic back to the SOM and to the AM62Ax processor itself. You should find that this signal is accessible at the processor ball number B10, named WKUP_CLKOUT0.
Looking up the WKUP_CLKOUT0 processor pad within the AM62Ax Datasheet, we can see that this pad is configured within the MCU_PADCONFIG33 register which has the memory address 0x04084084.
We can read this register like so:
Target (Linux)
devmem2 0x04084084
We should see the following output by default:
Example Output
root@phyboard-lyra-am62axx-2:~# devmem2 0x04084084 /dev/mem opened. Memory mapped at address 0xffff9fc5f000. Read at address 0x04084084 (0xffff9fc5f084): 0x08014000
The value held in the MCU_PADCONFIG33 memory address is 0x08014000, which can be broken down according to the MCU_PADCONFIG33 Register Field Descriptions within the TRM (see Table 14-7176). Here we can see that the register is in its reset state and is configured as an output, without any internal pull up/down resistors, and mux mode 0. This isn’t the mux mode we want so we will need to configure that before using this pin to drive our LED.
Modify the MCU_PADCONFIG33 register in order to configure the WKUP_CLKOUT0 as the desired GPIO mux mode we need (MCU_GPIO0_23):
Target (Linux)
devmem2 0x04084084 w 0x08014007
Writing the value 0x08014007 to MCU_PADCONFIG33 effectively changes the pad config settings, giving us the signal we want in the mode we need.
Run the Blink Program
Once you have the blink executable built and the processor pin is correctly multiplexed to bring out the signal MCU_GPIO0_23 as an output, we can connect up an LED to X_WKUP_CLKOUT0 and blink it!
Reference the following circuit diagram to help you connect up an LED to pin 9 of the X17 Expansion Connector on the phyCORE-AM62Ax Development Kit carrier board:
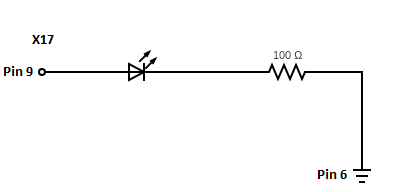
Now run the blink executable and watch the LED blink on and off!
Target (Linux)
./blink
To end the program, use Ctrl + C.